Jump to
Parameters
- Maximum number of particles: npmax
- Particle diameter: dp
- Particle density: rhop
- Fluid density: rhof
- Particles flow rate: PFR (number of particles entering per second)
- Particle inlet velocity: up_in
- Two-way coupling(Boolean): use_twoway
Define a derived data type for particle with following detail
- double x, y : position
- int i,j : mesh location
- double u,v : velocity
- double dt : Time step size
- int or boolean stop: active or not
Create an array of particles part, ptmp
Identify the current mesh location(i,j) of the particle based on particle position
This is rather easy in a structured grid compared to an unstructured one. The idea is particle would be somewhere near to the location it was at the previous time step. Hence we shall search the immediate four(in 2D) neighbours and if not found, search neighbours’ neighbours.
Algorithm
- grab the old location: iold, jold
- grab the current position: xp, yp
- define now location: inew, jnew
- Search to the right: do while (xp >=x(inew+1) && inew+1 <= nx); inew=inew+1;
- Search to the left: do while (xp <= x(inew) && inew-1>= 1 ); inew=inew-1;
- Either of the above search will only execute.
- Do the same for yp
Bilinear interpolation
The new location we arrive is marked in the figure below. Linearly interpolate for U & V.
U_{P} = \frac{U1*Green+U2*Purple+U3*Yellow+U4*Red}{Green+Purple+Yellow+Red}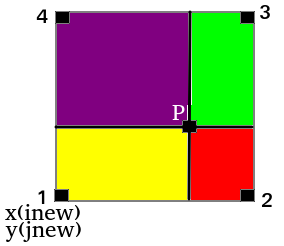
wx1=(x0-x (i))/(x (i+1)-x (i)); wx2=1.0_WP-wx1
wy1=(y0-ym(j))/(ym(j+1)-ym(j)); wy2=1.0_WP-wy1
// Rectangular area in a matrix
ww(1,1)=wx1*wy1
ww(2,1)=wx2*wy1
ww(1,2)=wx1*wy2
ww(2,2)=wx2*wy2
//Bilinear interpolation of U
myu=sum(ww*U(i:i+1,j:j+1))Particle initialisation
particles to be added nadd = PFR*dt
for 0:nadd, do the following
- nadded++, np++
- give x position that of inlet
- y position random between y(1) and y(ny)
- locate i,j using previously defined plocate algorithm
- If any particle are in wall (mask ==1), remove that particle (nadded++, np++)
- Initialise u velocity to the particle
ODE solver for a single particle: Second order Runge-Kutta
Step 1: Predictor (Forward Euler) : \phi^{n+\frac{1}{2}} = \phi^{n} + \frac{\Delta t}{2}f(\phi^{n})
Step 2: Corrector (Centered in time) : \phi^{n+1} = \phi^{n} +\Delta tf(\phi^{n+\frac{1}{2}})
Algorithm
for each particle p
Predictor – Euler prediction
- copy p to pn
- Calculate drag(dragx and dragy) by calling lpt_drag(dragx,dragy).
- p.x = pn.x +0.5*p.dt *p.u
- p.y = pn.y +0.5*p.dt *p.v
- p.u = pn.u +0.5*p.dt *(dragx+gravity_x+collision_x)
- p.v = pn.v +0.5*p.dt *(dragy+gravity_y+collision_y)
Corrector – Midpoint rule
- Recalculate drag(dragx and dragy) by calling lpt_drag(dragx,dragy).
- p.x = pn.x +p.dt *p.u
- p.y = pn.y +p.dt *p.v
- p.u = pn.u +p.dt *(dragx+gravity_x+collision_x)
- p.v = pn.v +p.dt *(dragy+gravity_y+collision_y)
call plocate to relocalize particle on mesh
Update optimal timestep size p.dt=taup
Drag Model (lpt_drag(dragx,dragy).)
Step 1: Obtain particle velocity by interpolation. Input: i,j,x,y Output: u,v
ug=get_u(p.i,p.j,p.x,p.y) and vg=get_v(p.i,p.j,p.x,p.y)
Step 2: Calculate Stokes response time
taup=dp^2/(18.0*knu)
Step 3: Calculate particle Reynolds number
Re_{p} = \sqrt{[p.u - u_{g}]^{2} +[p.v - v_{g}]^{2} } . \frac{dp}{knu}Step 4: Shiller & Naumann drag correlation
taup=taup/(1.0+0.15*Rep*(0.687))
Step 5: Acceleration due to drag
accx=(ug – p.u)/taup
accy=(vg – p.v)/taup
accx, accy are dragx and dragy
two way coupling
For two-way coupling, add momentum source term calculated from particle to the u* calculation in the velocity step.
// Increment exchange term
if (mask(myp%i,myp%j).eq.0) then
loading=rhop*Pi/6.0_WP*dp**3/(rhof*d**3)//ratio of particlemass tot fluid mass
tmpU(myp%i,myp%j)=tmpU(myp%i,myp%j)-mydt*dragx*loading
tmpV(myp%i,myp%j)=tmpV(myp%i,myp%j)-mydt*dragy*loading
end if
// Transfer source to flow solver
if (use_twoway) then
do j=1,ny
do i=2,nx
if (maxval(mask(i-1:i,j)).eq.0) srcU(i,j)=srcU(i,j)+0.5_WP*sum(tmpU(i-1:i,j))
end do
end do
do j=2,ny
do i=1,nx
if (maxval(mask(i,j-1:j)).eq.0) srcV(i,j)=srcV(i,j)+0.5_WP*sum(tmpV(i,j-1:j))
end do
end do
end if
//In velocity_step
// Adams-Bashforth
U=U+HU1+ABcoeff*(HU1-HU2)+srcU
V=V+HV1+ABcoeff*(HV1-HV2)+srcV